Stepping out of the darkness into light. That’s how patients are describing their experience after participating in a CIRM-funded clinical trial targeting a rare form of vision loss called retinitis pigmentosa (RP). jCyte, the company conducting the trial, announced 12 month results for its candidate stem cell-based treatment for RP.
RP is a genetic disorder that affects approximately 1 in 40,000 individuals and 1.5 million people globally. It causes the destruction of the light-sensing cells at the back of the eye called photoreceptors. Patients experience symptoms of vision loss starting in their teenage years and eventually become legally blind by middle age. While there is no cure for RP, there is hope that stem cell-based therapies could slow its progression in patients.
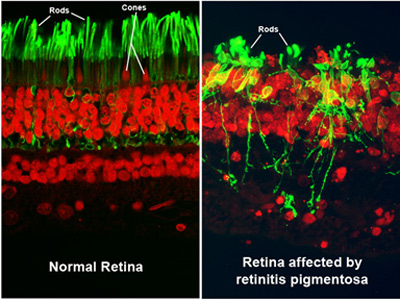
Photoreceptors look healthy in a normal retina (left). Cells are damaged in the retina of an RP patient (right). (Source National Eye Institute)
jCyte is one of the leaders in developing cell-based therapies for RP. The company, which was founded by UC Irvine scientists led by Dr. Henry Klassen, is testing a product called jCell, which is composed of pluripotent stem cell-derived progenitor cells that develop into photoreceptors. When transplanted into the back of the eye, they are believed to release growth factors that prevent further damage to the surviving cells in the retina. They also can integrate into the patient’s retina and develop into new photoreceptor cells to improve a patient’s vision.
Positive Results
At the Annual Ophthalmology Innovation Summit in November, jCyte announced results from its Phase 1/2a trial, which was a 12-month study testing two different doses of transplanted cells in 28 patients. The company reported a “favorable safety profile and indications of potential benefit” to patient vision.
The patients received a single injection of cells in their worst eye and their visual acuity (how well they can see) was then compared between the treated and untreated eye. Patients who received the lower dose of 0.5 million cells were able to see one extra letter on an eye chart with their treated eye compared to their untreated eye while patients that received the larger dose of 3 million cells were able to read 9 more letters. Importantly, none of the patients experienced any significant side effects from the treatment.
According to the company’s news release, “patient feedback was particularly encouraging. Many reported improved vision, including increased sensitivity to light, improved color discrimination and reading ability and better mobility. In addition, 22 of the 28 patients have been treated in their other eye as part of a follow-on extension study.”
One of these patients is Rosie Barrero. She spoke to us earlier this year about how the jCyte trial has not only improved her vision but has also given her hope. You can watch her video below.
Next Steps
These results suggest that the jCell therapy is safe (at least at the one year mark) to use in patients and that larger doses of jCell are more effective at improving vision in patients. jCyte CEO, Paul Bresge commented on the trial’s positive results:
Paul Bresge
“We are very encouraged by these results. Currently, there are no effective therapies to offer patients with RP. We are moving forward as quickly as possible to remedy that. The feedback we’ve received from trial participants has been remarkable. We look forward to moving through the regulatory process and bringing this easily-administered potential therapy to patients worldwide.”
Bresge and his company will be able to navigate jCell through the regulatory process more smoothly with the product’s recent Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The FDA grants RMAT to regenerative medicine therapies for serious diseases that have shown promise in early-stage clinical trials. The designation allows therapies to receive expedited review as they navigate their way towards commercialization.
jCyte is now evaluating the safety and efficacy of jCell in a Phase2b trial in a larger group of up to 85 patients. CIRM is also funding this trial and you can read more about it on our website.
Related Links:
- jCyte starts second phase of stem cell clinical trial targeting vision loss
- Throwback Thursday: Progress to a Cure for Blindness
- A patient perspective on how stem cells could give a second vision to the blind

The dedication of the researchers at Jcyte and CIRM to the RP community is unparalleled and thank you seems so insufficient. Nevertheless, thank you! This study’s results truly give new hope that the encroaching darkness may stop.
Hi.i was diagnosed with rp in2016 at the age of 28.am eagerly waiting for new treatment to stop its progress.if you need I will be part of your research.am a medical student.now persuing my MD pharmacology.please inform further development in treatment.
Hope that Phase 3 will be success and it will end the suffering of millions of people across the world. Fingers crossed